How to Maintain pH and EC in Hydroponics System
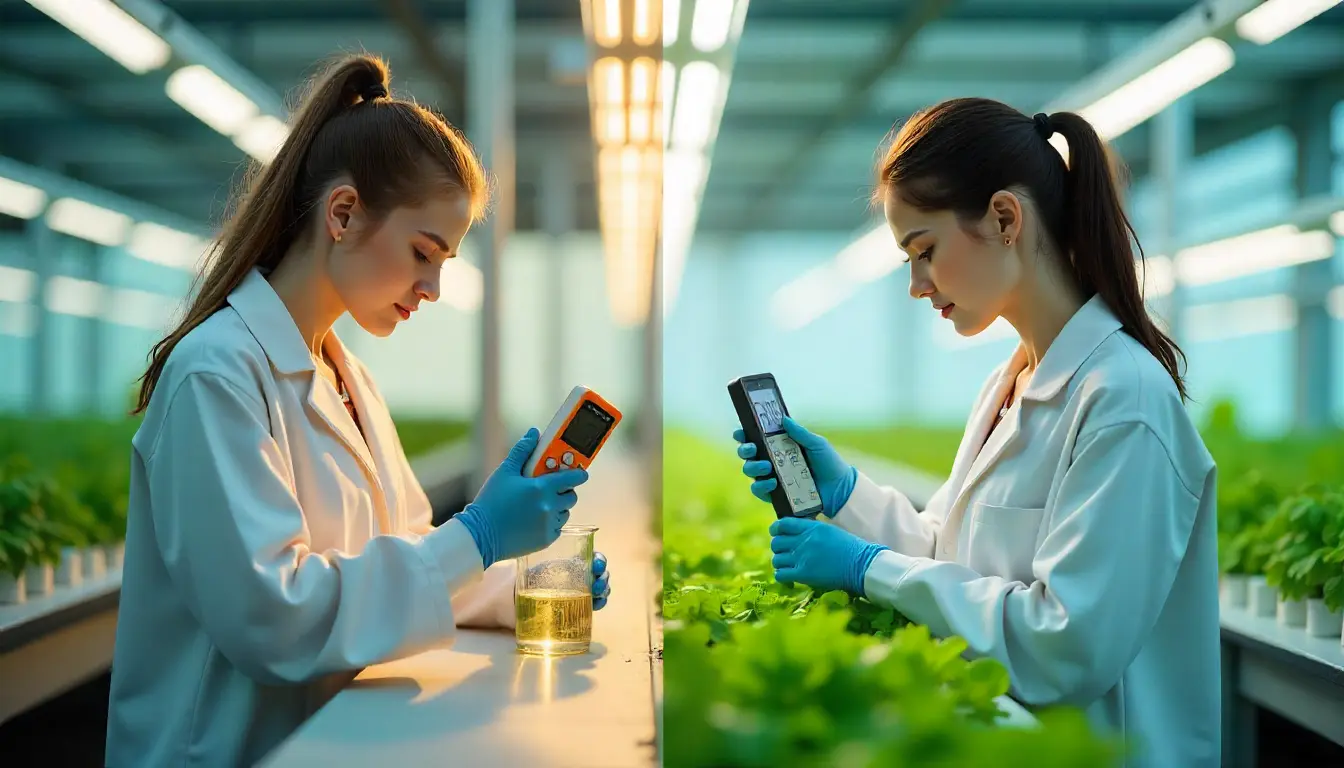
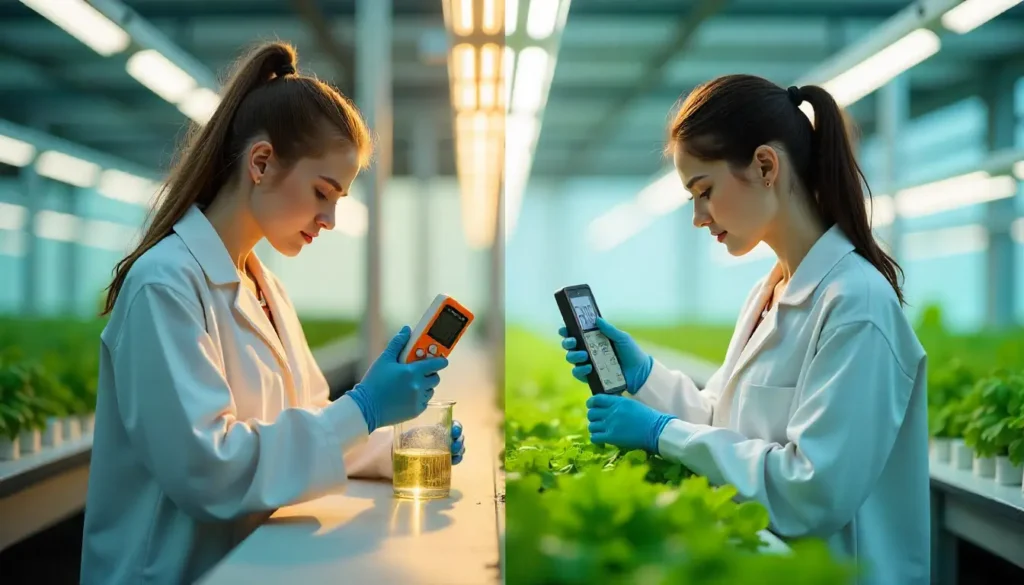
To demystify nutrient management in a hydroponic system, it’s essential to grasp the critical roles of pH and Electrical Conductivity (EC) which are the two pillars of a healthy nutrient solution. Unlike soil-based farming, where natural buffering occurs, hydroponics relies entirely on water-soluble nutrients. This makes it both efficient and highly sensitive.
It becomes tricky when all the nutrients in the system are supplied through a nutrient solution and identifying nutrient deficiency or abnormalities becomes a real challenge. The symptoms, such as yellowing of leaves, stunting, and browning of leaf edges, are all symptoms of nutrient disorder, but identical visuals make our work difficult. So it’s best to take early precautions by properly monitoring the pH and Electrical Conductivity and make amendments at the right time.
First, we need to understand what pH and Electrical Conductivity do to a plant and how we can control them.
Role of pH in Hydroponics
pH stands for “potential of Hydrogen” and is a scale used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, where pH 7 is neutral (pure water), below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is alkaline (basic). The right pH is essential for ‘nutrient absorption’, as nutrients are available to plants only in ionic form or dissolved form within a particular range. Outside that range, these ions can react with each other or other ions, which can cause ‘ Nutrient lock’ situations. It might be due to overfeeding or hard water used in the system which either causes deficiency or inevitable toxicity.
Most of the hydroponics functions best within a slightly acidic pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. Some plants may perform better in slightly different ranges, but this is applicable for most of the crops.
How to Maintain pH in Hydroponics System
Unlike soil, hydroponics doesn’t have a self-buffer system, which allows for small fluctuations and self-repair. To correct the pH we need to add some chemicals in the mixing tank to balance it.
The visual symptoms of low pH includes yellowing, stunted growth, browning of leaves or mushiness of roots due to deficiency of Phosphorus, Magnesium and calcium deficiency or toxicity of Iron or Magnese, while symptoms on high pH includes interveinal chlorosis, the leaves were yellow between the leaf veins, brown or yellow spotting, gradual necrosis and wilted or curled leaves and elements like Iron, calcium and phosphate precipitates out or deficiency of copper and zinc occurs.

Reclamation of acidic solution
One can use Potassium phosphate (K3PO4), a weak base to increase the pH levels. Although we suggest using a pH Up solution, which typically contains potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide, it is a strong base, so every added dose should be monitored carefully in 1:10(one part of basic solution and 10 parts of distilled water).
Reclamation of the basic solution
Usually, basicity increases due to continuous use of hard water and phosphoric acid, or shop-bought pH adjuster is used in the Hydroponics mix in diluted form in 1:10 (1part of acid and 10 parts of distilled water) to reclaim the nature of the mixture. Use the solution gradually, let the acid mix slowly, and keep measuring pH with every dose added to the mix. Use nitric acid for the same during the growing season, as phosphoric acid is suggested after the plant is fully grown. It will be a ‘game over’ if you use acid even the slightest above the recommended level. Keep adjusting the solution until it meets the requirements.
What is Electrical Conductivity?
EC or Electrical Conductivity is a measure of the food available to the plant in ionic form. These ions allow a flow of electricity in water. It is measured in milliSiemens per centimetre, but, unlike pH, there is no universal scale to measure it, so we have four options as conductivity scales:
- PPM (Parts per Million) [EC x 700]
- TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) or DS (Dissolved Salts) or MS (Measured Salts); otherwise known as PPM 500 [EC x 500]
- EC (Electrical Conductivity) [1 mS/cm2 = 1 EC]
- CF (Conductivity Factor) [EC x 10]
The EC needs for each crop are different, so we must keep those numbers in mind. EC doesn’t have a role in understanding the number of nutrients present in the system, but it affects your plant’s ability to take up water. In addition, the EC level fluctuates every day, so it’s best to monitor it daily and make changes accordingly.
Change the nutrient solution every seven to ten days after cleaning the container, to remove all precipitated salts and prevent diseases. If the EC levels in the solution are too low, then symptoms like Leaf discolouration, Holes in leaves or brown spots of necrosis, Stunted roots and growth, Difference in crop yield
Stunted, twisted, or misshapen leaves. Or if the EC levels are too high, your plant may experience toxicity with poor necrotic value.
How to increase EC in Hydroponics System?
The EC can be increased, simply by adding fertilizer solutions or Nutrient solutions. Make sure you are measuring EC on every addition and every day, as excessive solution may lead to toxicity.
How to decrease EC in Hydroponics System?
You can simply add more water to the nutrient solution to decrease the EC level. If the concentrations are too high, it is best to flush the whole system and refill it with the required solution. As the EC becomes too high, rinse the roots and container.

Conclusion
Nutrient absorption in hydroponics is deeply influenced by pH and EC levels, and maintaining them within the optimal range is essential for healthy plant growth. While fluctuations are common, they’re manageable with regular monitoring and timely adjustments. Fortunately, plants often give us clear signals, through leaf color, growth patterns, or other visible symptoms, allowing us to respond before serious issues arise. By understanding the role of pH and EC, we are not just managing water chemistry, we create a balanced, thriving environment for our crops. I hope this article has helped simplify the process and given you the insights you always needed for your system. A few minutes of attention each day can go a long way in ensuring consistent growth, better yields, and happier plants.
Latest Post
- Nutrients Required for Hydroponic Farming
- Types of Grow Light for Hydroponics
- Factors Affect Nutrient Solution in Hydroponics
- How to Maintain pH and EC in Hydroponics System
- How to Clean Hydroton Clay Pebbles For Reuse
- How to Clean Hydroton Clay Pebbles for Reuse
- Role of Grow Light in Hydroponics
- How to Grow Hydroponic Peppers (Bell Peppers Hydroponics)
- Aeroponics vs Hydroponics vs Aquaponics
- Difference between NFT and DFT Hydroponics : What’s best for you?
- Can You Grow Watermelon Hydroponically : Hydroponic Watermelon
- Best Vegetables for Hydroponics System
Join Our Hydroponics Growers Group!
Connect with fellow hydroponics enthusiasts, share your ideas, ask questions, and grow together as a community.
👉 Join WhatsApp Group