How to Grow Hydroponic Garlic in Easy Way- A Modern Trend
Garlic is an important herb belonging to the Amaryllidaceae family and scientifically known as Allium sativum. Garlic has a bulb which is below the soil and contains cloves which are used in dishes and have many medicinal properties. From its phenotypic view its leaves are flat and long attached to the bulb which is composed of multiple cloves in a papery covering. Garlic has a very unique flavor. When it is added to dishes it provides a separate flavor which is not matchable with other spices. In medicinal properties it is found effective in cardiovascular problems. Hydroponic garlic is cultivated in a soil less system where the year round production is become possible without interference of climate.
Why Garlic is Important:
There are some aspects of importance of garlic in tables below:
Nutritional Aspects:
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g of Raw Garlic |
| Calories | 149 |
| Protein | 6.36g |
| Total Fat | 0.5g |
| Dietary Fiber | 2.1g |
| Carbohydrates | 33.06g |
| Sugars | 1g |
| Vitamin C | 31.2mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 1.235mg |
| Folate | 3μg |
| Calcium | 181mg |
| Iron | 1.7mg |
| Magnesium | 25mg |
| Phosphorus | 153 mg |
| Potassium | 401mg |
| Manganese | 1.7mg |
| Selenium | 14.2μg |
Other Aspects:
| Aspect | Benefits |
| Culinary Versatility | Enhances flavor in various dishes; a staple in global cuisines |
| Medicinal Properties | Potential cardiovascular support; antimicrobial properties |
| Traditional and Cultural Significance | Used in rituals and cultural practices in various traditions |
| Economic Importance | Major global crop with significant contributions to agriculture and trade |
| Value-Added Products | Production of garlic powder, garlic oil, and supplements adds value to the food and health industries |
| Employment Opportunities | Cultivation, harvesting, and processing provide jobs in different regions |
| Global Trade | Contributes to international trade, supporting the global economy |
| Health and Wellness Industry | Recognized for potential health benefits, contributing to the wellness sector |
How to Grow Hydroponic Garlic | How Can You Grow Garlic in Hydroponics:
Selection for Hydroponic System:
To grow garlic using hydroponics, you can choose systems like Deep Water Culture (DWC), Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), or Aeroponics. In DWC, garlic sits in nutrient-rich water, and in NFT, a thin layer of water flows over the roots. Aeroponics involves misting the roots with nutrients. Ensure the system has enough space for garlic bulbs to grow. You can also use vertical setups or Drip Systems, but make sure there’s ample room for bulb development. Experiment and adjust as needed for successful hydroponic garlic growing.
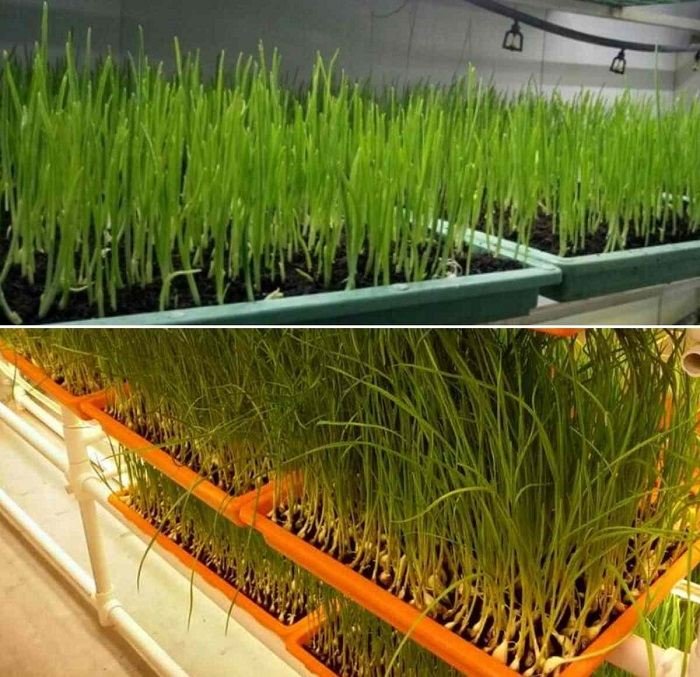

Image Source: Gardening tips
Varieties of Garlic Suitable for Hydroponics:
| Variety | Suitability for Hydroponics |
| California Early | Well-suited due to early maturity and large cloves |
| California Late | Adaptable for hydroponic systems with a later maturity |
| Silver Rose | Suitable for hydroponics, mild flavor, and extended shelf life |
| Nootka Rose | Adaptable to hydroponics, slightly spicy flavor |
| Ajo Rojo | Known for adaptability to hydroponics, strong flavor |
| Shandong | Well-suited for hydroponics, smaller size for controlled environments |
Planting Material of Garlic in Hydroponics:
To cultivate garlic hydroponically, garlic cloves, sourced from healthy bulbs, serve as the primary planting material. Optimal garlic cultivation in hydroponics involves selecting suitable cloves, planting them in a hydroponic medium like coconut coir or perlite, and ensuring they are positioned correctly with the pointed end facing upward. The cloves are set in a hydroponic system such as Deep Water Culture (DWC), Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), or Aeroponics, with a nutrient-rich solution providing essential elements for garlic growth. Environmental conditions, including pH, EC levels, temperature, and humidity, are carefully monitored and adjusted to meet garlic requirements. Adequate lighting, either natural or supplemented with LED grow lights, contributes to the photosynthesis process.
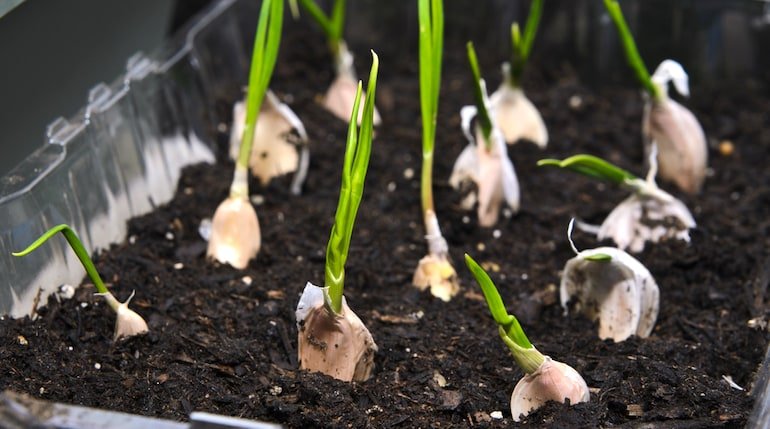

Image Source: Thompson & Morgan
Growing Medium for Healthy Root Development:
In hydroponic cultivation of garlic, various growing media can be utilized to provide support and foster healthy root development. Popular options include coconut coir, known for its water retention and aeration capabilities, perlite, a lightweight and sterile medium ensuring proper drainage, and vermiculite, offering good water-holding capacity and aeration. Rockwool, a sterile and stable option, is often used in cubes or slabs, while expanded clay pellets, such as Hydroton, provide a lightweight and well-draining medium. When selecting a growing medium for hydroponic garlic cultivation, factors like water retention, aeration, and pH neutrality or adjustability are crucial considerations, with experimentation to determine the most effective medium for a specific hydroponic system.
Nutrient Solution for Hydroponic Garlic:
In hydroponic systems, providing an appropriate nutrient solution is crucial for the successful cultivation of garlic. Commonly, hydroponic nutrient solutions consist of a balanced mix of macronutrients and micronutrients. Adjustments can be made as needed to maintain the solution within the appropriate range for garlic cultivation. Additionally, it’s advisable to follow manufacturer guidelines and conduct periodic checks to prevent nutrient imbalances and deficiencies in the hydroponic system, fostering healthy garlic growth.
Macronutrients:
| Nutrient | Function | Sources |
| Nitrogen (N) | Essential for leaf and stem growth, protein synthesis | Organic matter, fertilizers |
| Phosphorus (P) | Promotes root development, flower and fruit formation | Fertilizers, bone meal, rock phosphate |
| Potassium (K) | Supports overall plant health, water uptake, and disease resistance | Fertilizers, wood ash, compost |
| Calcium (Ca) | Strengthens cell walls, regulates nutrient uptake | Lime, gypsum, calcium-containing fertilizers |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Key component of chlorophyll, aids in photosynthesis | Epsom salt, dolomitic lime, fertilizers |
Micronutrients:
| Nutrient | Function | Sources |
| Iron (Fe) | Essential for chlorophyll formation, photosynthesis | Iron chelates, iron sulfate |
| Manganese (Mn) | Enzyme activation, nitrogen metabolism | Manganese sulfate, fertilizers |
| Zinc (Zn) | Involved in enzyme activity, hormone regulation | Zinc sulfate, zinc chelates |
| Copper (Cu) | Important for enzyme function, chlorophyll synthesis | Copper sulfate, copper chelates |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Facilitates nitrogen fixation, enzyme activation | Molybdenum-containing fertilizers |
| Boron (B) | Aids in cell division, sugar transport | Borax, boric acid, boron-containing fertilizers |
| Chlorine (Cl) | Involved in photosynthesis and osmosis | Found in soil and irrigation water |
| Nickel (Ni) | Facilitates enzyme activity | Naturally present in some soils |
EC and pH in Hydroponic Garlic:
Ensuring the success of garlic cultivation in hydroponics involves maintaining the correct pH and electrical conductivity (EC) levels in the nutrient solution. Ideally, the pH should be kept within the range of 6.0 to 6.5, creating a slightly acidic to neutral environment that enhances nutrient availability and uptake by garlic roots. Concurrently, the recommended EC levels range from 1.2 to 2.5 mS/cm, with adjustments based on the specific growth stage, aiming for lower EC during vegetative growth and slightly higher levels during flowering and bulb development.
Temperature Management in Hydroponic Garlic:
Temperature is the most important factor which can be maintained in a hydroponic system. During germination and seedling phases, it is advisable to ensure temperatures ranging from 70°F to 75°F (21°C to 24°C) to encourage robust root establishment. In the vegetative growth stage, maintaining a temperature between 60°F to 70°F (15°C to 21°C) supports healthy foliage development and efficient photosynthesis. As garlic progresses to the bulb formation stage, slightly cooler temperatures ranging from 55°F to 65°F (13°C to 18°C) are recommended, contributing to enhanced bulb enlargement and quality.
Humidity:
Optimal humidity levels are essential for successful hydroponic garlic cultivation, impacting various growth stages. Higher humidity, approximately 70-80%, is advantageous during germination and seedling phases, supporting robust root establishment and initial growth. In the vegetative stage, slightly lower humidity, ranging from 60-70%, is recommended to prevent excess moisture around the foliage and mitigate the risk of fungal diseases. Lower humidity levels, around 50-60%, during the bulb formation stage promote optimal bulb development and reduce the likelihood of diseases, ensuring the overall quality of the garlic crop.
Lighting:
Successful hydroponic cultivation of garlic relies heavily on meeting the lighting requirements of the plants. When cultivating garlic hydroponically, it’s imperative to guarantee a consistent supply of adequate light throughout various growth stages. Whether through natural sunlight exposure or the use of supplemental artificial lighting like LED grow lights, maintaining optimal light conditions is key to fostering healthy foliage, robust bulb formation, and achieving an overall superior crop quality.
Pruning in Garlic:
Pruning in hydroponic garlic cultivation involves the removal of specific plant parts to enhance overall bulb development and improve resource allocation. Pruning of yellow leaves and dried matter from the plants leads to a healthy production and growth. Sometimes curly flower stems emerge from the plants leading to the seed production which can be removed so that the plants energy is diverted to the bulb production, not for the seed production. Pruning is typically performed throughout the growth cycle, allowing hydroponic garlic growers to maintain plant vigor, maximize bulb size, and achieve a higher quality harvest.
Harvesting Practice in Hydroponic Garlic:
Harvesting garlic in hydroponics involves carefully timing the process to ensure optimal bulb development. The ideal time to harvest garlic is when the lower leaves start to turn yellow and die back, indicating that the bulbs have matured. In hydroponics, this often occurs around 8 to 10 months after planting, depending on the garlic variety and specific growing conditions. To harvest, gently unearth the garlic bulbs, ensuring that the roots are intact. Shake off excess growing medium and remove any loose outer layers. After harvesting, garlic bulbs should be cured by allowing them to dry in a well-ventilated, shaded area for about 2-3 weeks.
Image Source: wikiHow
Conclusion:
So we see all the requirements, procedures, systems, varieties of garlic for the production in hydroponics. As we see this system is highly based on management of different aspects like controlling temperature, humidity, light, and also the nutrient solution. One who opt this system must take a training program or should take guidance from a recognized university or scientists or companies which teaches to handle this whole system. As per the production, it is very successful due to its convenience of indoor facilities and without the interference of climate garlic can be grown throughout the year.







